THE EQUINE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
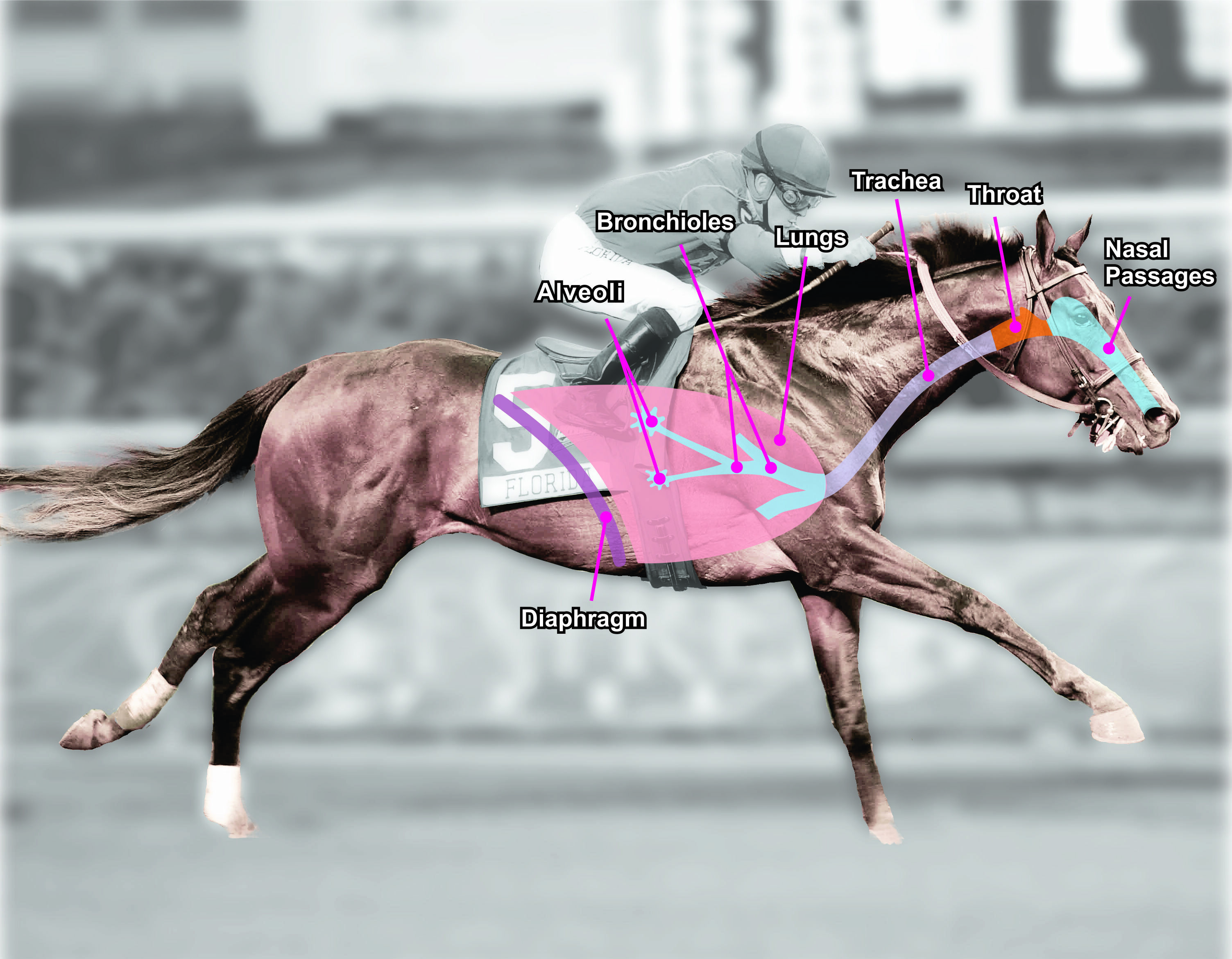
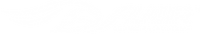
Oxygen provides the body with energy to power exercise. The equine respiratory system is responsible for bringing oxygen in to the body. It starts at the nostrils and ends at the lungs. When a horse inhales, outside air passes through the nasal passages, past the throat, down the trachea and into the lungs deep into the alveoli (or air sacs). There, the oxygen in the air diffuses into the pulmonary capillaries to be transported throughout the body to provide energy for exercise. Energy for exercise comes from a molecule called ATP, which is most efficiently made in the body using oxygen. The waste product of energy is carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is transported out of the body by taking the reverse pathway. Blood carries carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs, where it passes through the pulmonary capillaries, into the alveoli and is exhaled out of the body. The diaphragm is a muscle used to expand and contract the lungs to draw air in push air out.
HORSES BREATHING IN AIR
By the time a horse crosses the finish line in a 5-furlong race, has completed a Grand Prix show jumping round, or gone 1/6th of the way around a 3-star cross-country course, it will have moved around 1,800 liters (475 gallons) or six bathtubs of air in and out of its lungs. This equates to moving two buckets of air in and out of the lungs every second!
The air inhaled into the horse’s respiratory system during a 5-furlong race consists of about 380 liters (100 gallons) of oxygen (the rest is made up of nitrogen) and only a quarter of that air (95 liters) will be absorbed into the blood. The oxygen absorbed by the lungs is used to perform the process of aerobic metabolism, which gets the energy from stored glucose (carbohydrates) into the muscle cells. Of the total amount of energy the horse needs to get from the starting gate to the finish line in a 5-furlong race, around 70% of this will come from aerobic metabolism (around 70% for show jumping and 90% for cross-country).
The remaining energy comes from anaerobic metabolism, which also breaks down glucose to generate energy, but can be done without oxygen. Anaerobic metabolism is a fast process but is inefficient because it can only be used for a short time due to the buildup of lactic acid. Even in a race or jumping round lasting less than a minute, the majority of the energy generated must come from using oxygen to “burn” carbohydrates.
The harder a horse works, the more oxygen it needs and the more air it must move in and out of the lungs. If a horse doubles its speed, it will need to double the amount of air moved in and out of the lungs.
FLAIR® Strips reduce resistance to breathing to make it easier for horses to bring air into the lungs by supporting the soft tissues overlying the nasal passages, to support optimal respiratory system function.
INHALING OXYGEN
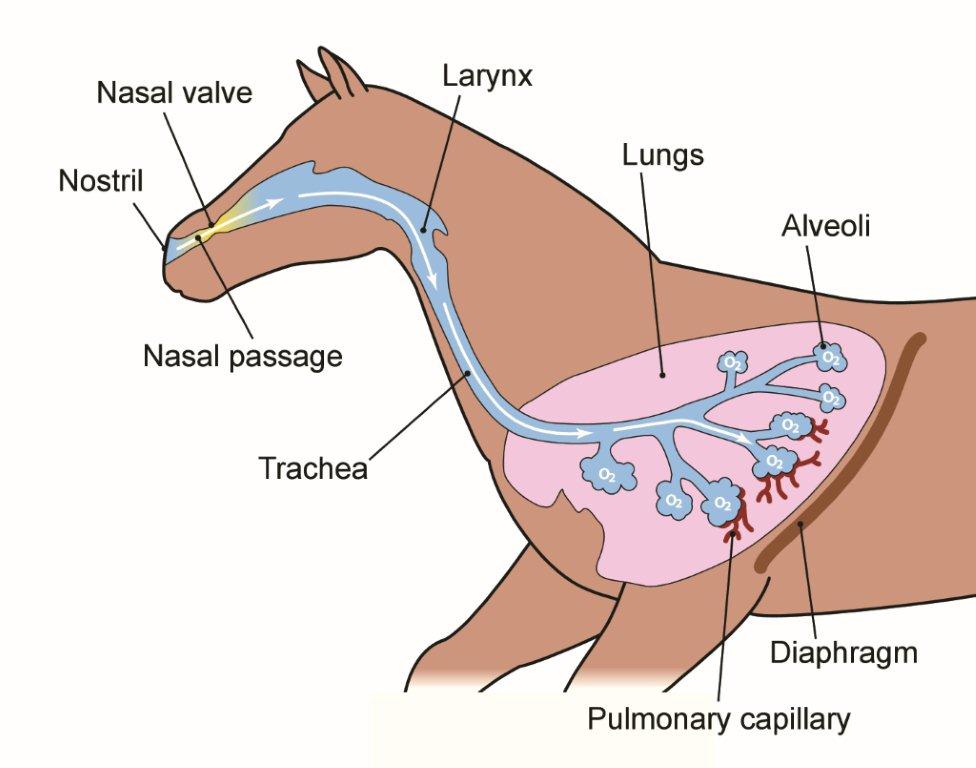
As illustrated above, air enters the body by first passing through the horse’s upper respiratory system - including the nostrils, the nasal passages, the larynx, then through the trachea (windpipe) - before moving into the lower respiratory system - the airways and alveoli (air sacs) in the lungs.
The horse’s windpipe is approximately 5-8 centimeters in diameter near the larynx, but as it passes deeper in the lung it begins to divide to produce smaller and smaller airways, much like a tree on its side. At the level of the smallest airways, after perhaps 25 divisions, the airways are fractions of a millimeter in size.
When the air gets to this point in the chain from nostril to muscle cell, the oxygen in the air has to cross from the air space (“alveoli”) into the pulmonary capillaries (tiny blood vessels in the lungs). At this stage, the membranes separating the oxygen containing air in the alveoli from the red blood cells in the capillaries are only the thickness of 1/100th the width of a human hair.
The oxygen transfers from the alveoli across this thin membrane and into the blood by diffusion. The total area for oxygen to diffuse across the horse’s lung is equivalent to the area of 10 tennis courts!
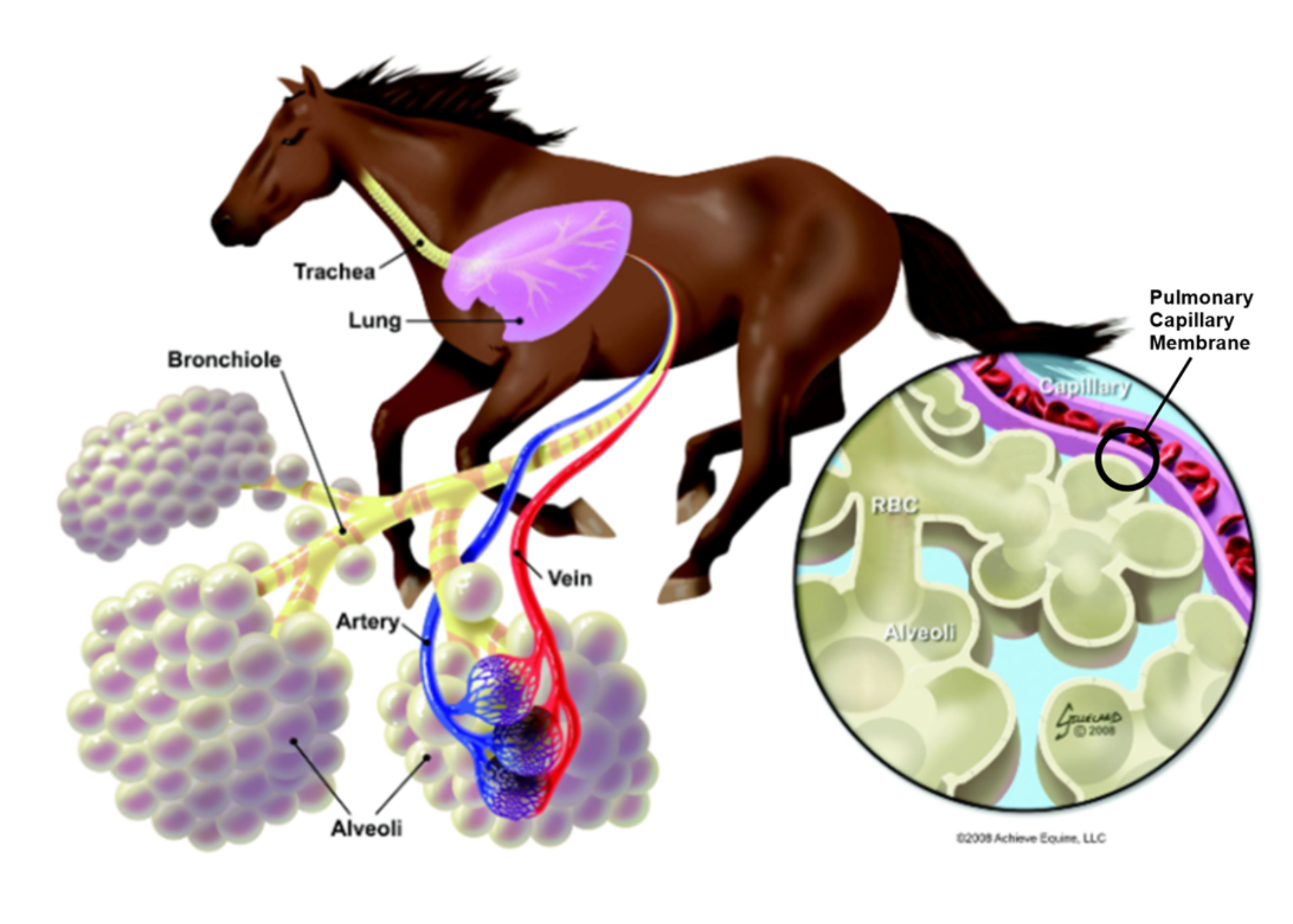
The PCM that the oxygen must transfer across are so thin that they can rupture under the stress of exercise. When this happens, red blood cells spill from the capillaries into the alveoli. This is known as lung bleeding or exercise induced pulmonary hemorrhage (EIPH).
Several independent clinical studies show that by reducing airflow resistance at the nasal passages, specifically at the nasal valve with the use of FLAIR Strips, these PCM ruptures — and thus bleeding — are reduced.
TRANSFERRING OXYGEN THROUGHOUT THE BODY
Once in the bloodstream, the oxygen is bound to hemoglobin (the molecule inside red blood cells that makes blood red) and the oxygen-rich blood is pumped around the body by the heart. This oxygen-rich blood must then reach the muscles to provide energy. At the muscle, the reverse process takes place with oxygen leaving the red blood cells and crossing into the muscle cells, again by diffusion. Finally, in the muscle cells, the oxygen moves to a sub-unit of the cell (“organelle”) called the mitochondria. By the time it gets inside the mitochondria, the level of oxygen may only be around 1/80th of that in the air outside the horse!
Efficient oxygen transfer from the airways to the red blood cells is very important in maximizing energy and a horse's ability to exercise. Some of the best racehorses (especially those racing over middle and longer distances) have large hearts and/or a high capacity to use oxygen.
FLAIR Strips help horses with even the biggest hearts and greatest capacity use the oxygen that they bring in as efficiently as possible.
EXHALING CARBON DIOXIDE
A well-functioning respiratory system in a horse is important for maximizing energy and getting rid of carbon dioxide – a waste product produced within the mitochondria of muscle cells during exercise. This process is effectively the same as bringing oxygen in but in reverse - carbon dioxide moves out of the cells by diffusion. When blood reaches the lungs, the carbon dioxide diffuses across the PCM, into the alveoli, and through the airways. The carbon dioxide is then breathed out during exhalation. It’s important to exhale carbon dioxide quickly; otherwise, the carbon dioxide can build up and contribute to fatigue.
FILTERING FROM LUNGS
The lungs are a very important filter for the horse’s body. All the blood in circulation passes through the lungs when it comes back in the veins after being pumped around the body through the arteries. Lungs have a better capacity to deal with bubbles and clots than most other organs in the body; so, it’s the ideal place to filter out any small blood clots (thrombi) or gas bubbles (emboli). While it’s not great to have a gas bubble in the lung (pulmonary embolism), it’s still highly preferable for this to go through the lung and be filtered rather than lodging in a coronary (heart) vessel or the brain.
The lung is also able to activate or deactivate certain hormones in circulation. In some cases, the lung acts as an endocrine organ and releases hormones that can have effects on the whole body.
The skin, the lung, and the gastrointestinal tract are the body’s interfaces with the outside world. Therefore, the lung has a highly developed immune system, different from that in other parts of the body, with specialized types of white blood cells to deal with things that could be inhaled, such as particles, bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
REGULATING BODY TEMPERATURE
An important but often overlooked function of the horse’s respiratory system is regulating body temperature. If a horse is taken from a cool climate to a warmer climate, he can increase his breathing rate at rest. Respiratory heat loss is an important thermoregulatory mechanism for the horse. Although it is commonly believed that horses blow after exercise because they are trying to get more oxygen into the blood, they are actually trying to regulate how hot they are.
FLAIR Strips help horses recover quicker by bringing cooler external air in more efficiently.
To some extent, the horse is still an enigma. There is no other animal that can carry the weight of a person (often representing an extra 10-15% of its own body weight) and itself at speeds of up to 35 mph or more. So, it may not be surprising that the horse’s respiratory system displays some curiosities, especially when compared to humans. Learn more about the equine respiratory system from Dr. David Marlin.
MAKE YOUR HORSE’S BREATHING EASIER
FLAIR Strips are drug-free and scientifically proven to optimize your horse’s respiratory system function. To reduce EIPH, maximize energy and extend the performance career of your horse, order online or contact us to learn more.